Pharmacy Automation Devices Market Trends, Forecast, and Growth
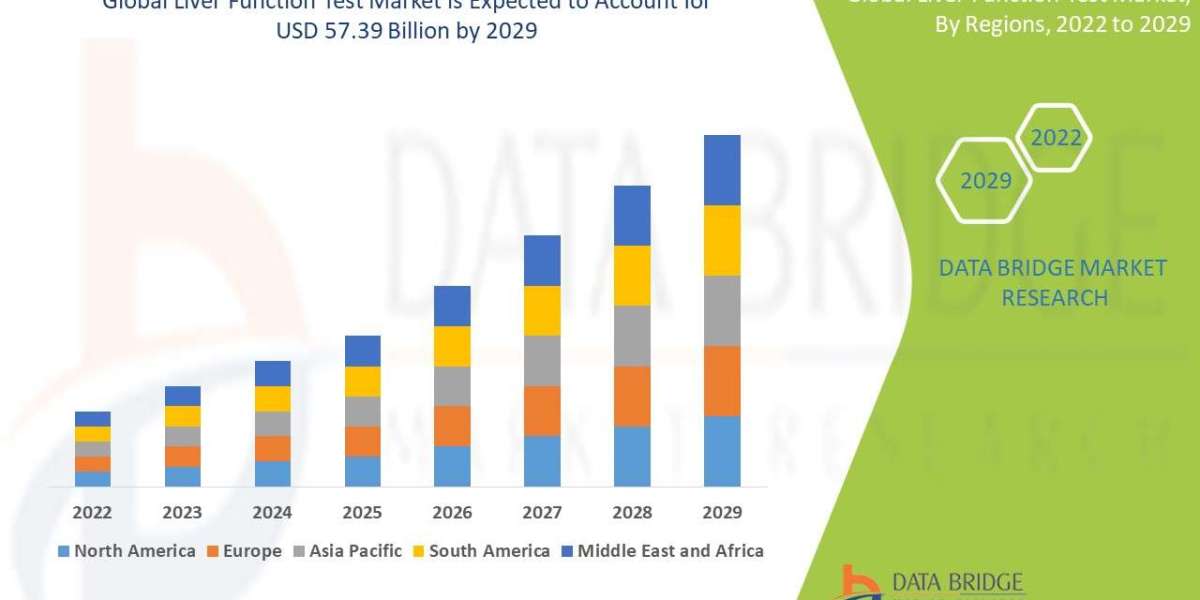
The global pharmacy automation devices market size was valued at USD 6.72 Billion in 2024 and is anticipated to grow from USD 7.32 Billion in 2025 to reach USD 14.48 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 8.9% during the forecast period (2025–2033). as reported by Straits Research. This trajectory reflects the market’s expanding potential, offering strategic opportunities for businesses, investors, and startups worldwide.
? Download a Sample Report
Explore a snapshot of the Market with our free report preview:? Download the Pharmacy Automation Devices Market Sample Report
Pharmacy Automation Devices Market Trends And Growth Drivers of 2025
Key factors fueling the growth of the market include:
Technological Innovation: Breakthroughs in technology are enabling new products and services, making Pharmacy Automation Devices Market solutions more accessible and effective.
Industry Adoption: Sectors such as Healthcare IT are adopting Pharmacy Automation Devices Market solutions to accelerate research, personalize treatments, and streamline clinical operations.
Global R&D Investments: Increased funding in research and development is accelerating market growth and encouraging new entrants.
Diversified Offerings: Companies are expanding portfolios to address new market segments and regional needs.
These drivers are creating a vibrant ecosystem where innovation and adoption reinforce each other, setting the stage for sustained growth.
Market Research and Methodology
Straits Research uses a multi-layered market research methodology to ensure credible and insightful data:
Top-Down and Bottom-Up Analysis for accurate market sizing
Data Triangulation to validate trends and eliminate bias
Primary Research involving interviews with industry leaders, manufacturers, and stakeholders
Limitations: Market fluctuations, data gaps, and currency volatility may affect forecasts.
Regional Outlook
North America (U.S., Canada): Leading innovation, strong R&D investments
Europe (Germany, UK, France): Mature infrastructure and regulatory backing
Asia-Pacific (China, India, Japan): Fastest-growing region due to industrialization
Latin America (Brazil, Mexico): Emerging opportunities driven by rising tech demand
Middle East & Africa: Early adoption phase, with long-term growth potential
Leading Companies Shaping the Pharmacy Automation Devices Market Include
- Amerisource Bergen Corporation
- Accu-Chart Plus Healthcare Systems Inc.
- Omnicell Inc
- McKesson Co.
- Pearson Medical Technologies
- Baxter
- Talyst LLC
- ScriptPro LLC
- CareFusion
- Fulcrum Pharmacy Management
- Health Robotics S.r.L.
- Medacist Solutions Group
- Aesynt Inc.
- Pyxis Corporation
- Kirby Lester
- Cerner Corporation
- ForHealth Technologies
- ARxIUM
- TouchPoint Medical
- Deenova S.r.L.
- Parata Systems LLC
Are recognized as the industry leader. These organizations are at the forefront of innovation, driving market expansion through strategic partnerships, product development, and customer engagement.
Segmentation of
The market is segmented to provide a detailed understanding of its structure and opportunities.
- By Product
- Medication Dispensing Systems
- Packaging and Labeling Systems
- Storage and Retrieval Systems
- Automated Medication Compounding Systems
- Tabletop Tablet Counters
- By End-Use
- Hospital Pharmacy
- Retail Pharmacy
Allows businesses to identify niche markets and tailor their strategies accordingly.
Key Findings and Insights
Market Size Growth: Detailed projections up to 2033
Regional Trends: Deep-dive into regional dynamics
Strategic Insights: Competitor positioning and market entry strategies
Technological Trends: Disruptive innovations and future-ready solutions
Forecast Analysis: Data-backed predictions from 2024–2033
Main Features of the Report
Comprehensive Market Insights: Detailed exploration of market dynamics, including growth drivers, trends, and challenges.
Historical and Forecast Data: Precise market size projections, revenue growth, and demand forecasts for key segments and regions.
Segmented Market Analysis: Insights into different market segments and their revenue potential, helping businesses identify new opportunities.
Actionable Intelligence: Guidance for businesses to make informed decisions and capitalize on emerging market trends.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the size of the Pharmacy Automation Devices Market?
The global pharmacy automation devices market size was valued at USD 6.72 Billion in 2024 and is anticipated to grow from USD 7.32 Billion in 2025 to reach USD 14.48 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 8.9% during the forecast period (2025–2033). As reported by Straits Research
2. What does the market research report cover?
The report provides a thorough evaluation of the current industry landscape, technological advancements, market trends, regional analyses, SWOT analysis and future growth opportunities.
3. What are some key insights included in the report?
The report covers market trends, technological innovations, purchasing volumes, pricing analysis, regulatory frameworks, and competitive intelligence, including analyses of major market players.
How to Access the Market Report
For those interested in exploring the market in greater detail, Straits Research offers several options:
Free Sample Report: Download a free sample to preview the insights and analysis available in the full report.
Full Market Report: Purchase the complete report for comprehensive analysis and actionable intelligence.
Market Segmentation Details: Access detailed segmentation data to better understand the market structure and opportunities.
You can find these resources on the Straits Research website, where you’ll also discover additional tools and analytics to support your market research needs.
Buy Global Market Report: https://straitsresearch.com/buy-now/pharmacy-automation-devices-market
About Straits Research
Straits Research is a global leader in market research, analytics, and advisory services. Our team of experienced analysts delivers actionable insights to help clients make informed, strategic business decisions. We offer tailored market research solutions to meet the unique needs of each client, ensuring they receive the most relevant and up-to-date market intelligence.
Contact Information
Email: sales@straitsresearch.com
Phone:
US: +1 646 905 0080
India: +91 8087085354
UK: +44 203 695 0409
Why Stay Informed About the Pharmacy Automation Devices Market?
As industries continue to evolve and innovation accelerates, the market stands out as a space full of promise. Whether you are a business leader, investor, or entrepreneur, staying informed about the latest market movements can provide a significant competitive advantage. Understanding growth potential, current trends, major players, and regional dynamics is essential for anyone looking to succeed in this dynamic market.