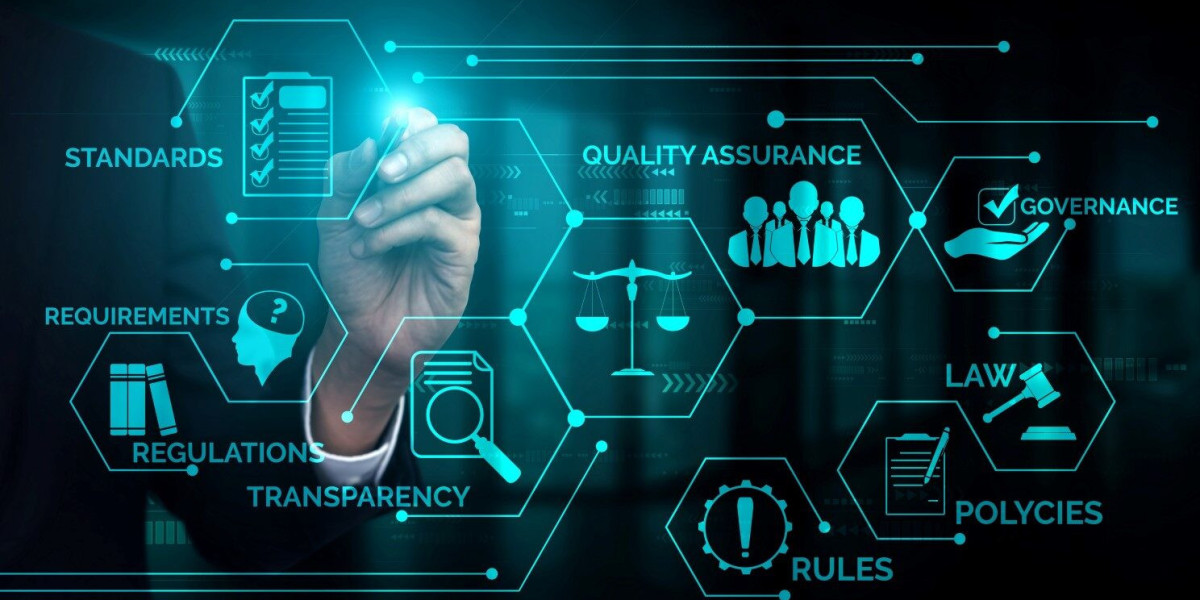
What Are the Basics You Need to Know About Regulatory Affairs?
In the complex landscape of industries ranging from pharmaceuticals to consumer goods, regulatory affairs play a pivotal role in ensuring compliance with governmental regulations. This field encompasses a wide array of responsibilities that are crucial for the safety, efficacy, and legality of products entering the market. Understanding the basics of regulatory affairs is essential for professionals aspiring to navigate this dynamic and critical sector.
Introduction to Regulatory Affairs
Regulatory affairs refer to the set of processes and practices that ensure products meet the required regulatory standards before they can be marketed or distributed. These standards are established by governmental agencies to safeguard public health and maintain product quality. Regulatory affairs professionals are tasked with interpreting, implementing, and ensuring compliance with these regulations throughout the product lifecycle.
Importance of Regulatory Affairs
The importance of regulatory affairs cannot be overstated, particularly in industries where product safety and efficacy are paramount. By adhering to regulatory requirements, companies mitigate risks associated with non-compliance, which can lead to costly delays, recalls, or even legal consequences. Moreover, regulatory compliance fosters consumer trust and confidence in products, which is crucial for long-term success in competitive markets.
Key Responsibilities in Regulatory Affairs
- Regulatory Strategy Development: Professionals in regulatory affairs formulate strategies to navigate the regulatory environment, ensuring timely approvals and compliance.
- Compliance Assurance: They ensure that all aspects of product development, manufacturing, and distribution adhere to applicable laws and regulations.
- Documentation and Submissions: Regulatory affairs professionals compile and submit necessary documentation to regulatory authorities to obtain approvals for product marketing.
Regulatory Affairs Education and Training
A solid educational background is essential for those entering the field of regulatory affairs. While specific requirements may vary by region and industry, a combination of scientific knowledge, legal understanding, and regulatory expertise is typically sought after. Many universities and institutions offer specialized programs or courses in regulatory affairs, covering topics such as:
- Regulatory Science: Understanding the scientific principles underlying regulatory requirements.
- Legal and Compliance Aspects: Learning about the legal frameworks and compliance obligations.
- Quality Assurance: Ensuring products meet quality standards throughout their lifecycle.
These educational programs often equip students with practical skills through case studies, internships, or simulations, preparing them to address real-world regulatory challenges.
Regulatory Affairs Careers
The field of regulatory affairs offers diverse career opportunities across various industries. Some common roles include:
- Regulatory Affairs Specialist: Responsible for preparing and submitting regulatory filings, ensuring compliance with applicable regulations.
- Regulatory Affairs Manager: Oversees regulatory strategies and manages a team of regulatory professionals.
- Quality Assurance Specialist: Focuses on maintaining quality standards and compliance throughout product development.
- Compliance Officer: Ensures adherence to regulatory requirements and company policies.
- Clinical Regulatory Affairs Manager: Manages regulatory activities related to clinical trials and submissions to health authorities.
Career paths in regulatory affairs often require continuous learning and staying updated with evolving regulations and industry standards. Professionals may also pursue certifications such as Regulatory Affairs Certification (RAC) to demonstrate their expertise and commitment to the field.
Regulatory Affairs in Different Industries
While pharmaceuticals and medical devices are commonly associated with regulatory affairs due to stringent safety and efficacy requirements, this discipline extends to various sectors:
- Food and Beverage: Ensuring food safety and labeling compliance.
- Cosmetics: Verification of product safety and ingredient labeling.
- Chemicals and Agrochemicals: Regulatory oversight to protect environmental and human health.
Each industry has its unique regulatory challenges and requirements, necessitating specialized knowledge and expertise from regulatory affairs professionals.
Challenges and Trends in Regulatory Affairs
The regulatory landscape is continuously evolving, presenting both challenges and opportunities for professionals in the field. Some current trends include:
- Global Harmonization: Efforts to standardize regulatory requirements across different regions.
- Digital Transformation: Utilizing technology for regulatory submissions and compliance monitoring.
- Emerging Technologies: Regulatory considerations for innovations such as gene therapies or artificial intelligence in healthcare.
Navigating these trends requires proactive engagement and adaptation to regulatory changes, ensuring products meet global standards while embracing innovation.
Conclusion
Regulatory affairs form the backbone of industries striving to deliver safe, effective, and compliant products to consumers worldwide. Aspiring regulatory affairs professionals should cultivate a deep understanding of regulatory requirements, pursue relevant education and training, and stay informed about industry trends. By embracing these fundamentals, they can contribute to regulatory compliance, consumer safety, and organizational success in an increasingly complex global market.
In essence, regulatory affairs is not just about adherence to rules but also about fostering innovation responsibly, ensuring that advancements in science and technology benefit society while meeting stringent regulatory standards. As the regulatory landscape continues to evolve, so too will the role and importance of regulatory affairs in safeguarding public health and product integrity.